
According to The Electrotechnical and Skills Partnership (TESP) we will require an additional 15,000 newly qualified electricians over the next 5 years in the UK, to ensure we have the skilled workforce to support the low carbon transition. This requires the recruitment of at least 12,000 electrical apprentices every year (up from an average of around 8,000 per year). One element of attracting and retaining this pipeline of talent is to ensure fair pay.
In the electrical industry the nationally bargained JIB rates are long established; however, in both 2022 and 2023 the lower rates were impacted by the rapidly increasing National Minimum Wage.
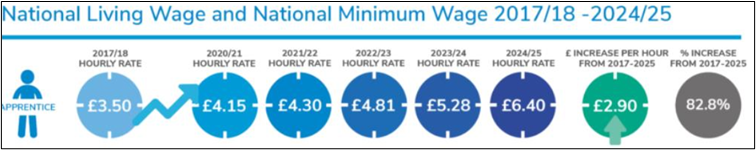
Since 2017 the apprentice rate, for those aged 16-18 or in the first year of their apprenticeship if older, has seen the largest proportional increase in the statutory rates at 82.8% over 8 years. Few, if any, industry schemes will have kept pace with this growth or predicted the increases, with the 2024 increase an inflation busting 21%.
 The Low Pay Commission (LPC), the independent body responsible for recommending National Living Wage increases to the government, provided a projection for 2025 of between a 1.8% and 6.5% increase. For apprentices however, the LPC describes the Government remit to “raise the minimum wage as high as possible without damaging the employment prospects of the affected workers.”
The Low Pay Commission (LPC), the independent body responsible for recommending National Living Wage increases to the government, provided a projection for 2025 of between a 1.8% and 6.5% increase. For apprentices however, the LPC describes the Government remit to “raise the minimum wage as high as possible without damaging the employment prospects of the affected workers.”
This will be difficult to judge given the need to encourage more employers to take on apprentices. Employers are consistently balancing the unique nature of apprenticeships, including the investment of training costs with wages, and not enough employers are opting to train. To maintain the number of electricians, we need annual apprentice recruitment to be 5% of the existing workforce each year, but the current average in both England and Wales is less than 4%.
There is also a need to consider market pay pressures. The TESP Labour Market Intelligence report 2023, highlights that demand for apprentices is likely to increase by 49% over the next 2 to 3 years. This trend is more pronounced in larger firms, which anticipate demand for apprentices will increase by 80%.
This future increased demand for apprentices is being complicated by declining birth rates coupled with the electrical industry struggling to attract females into the workforce, which means a smaller talent pool and an increasing war for talent. Meanwhile, over half (53%) of employers report that apprentices’ positions are currently hard or impossible to fill.
Despite the barriers, there is no doubt that increasing the number of electrical apprentices benefits the industry as well as individual businesses themselves. ECA, SELECT and Unite are now jointly reviewing the JIB rates to ensure that electrical apprentices are appropriately remunerated, considering the factors detailed above.
